Lost Wax Casting
Investment Casting, also known as Lost Wax Casting, is a metal parts manufacturing process that’s chosen based on factors like design requirements, cost, and feasibility. This article aims to provide insights into investment casting to aid informed decision-making.
Investment casting offers precise component production while minimizing material waste and energy usage. It’s particularly adept at producing intricate parts, making it valuable for design engineers.
In investment casting, a shell made of ceramic, plaster, or plastic surrounds a wax pattern. After melting and removing the wax pattern in a furnace, metal is poured into the shell to create the casting. The term “investment” in investment casting historically refers to the shell “clothing” or “surrounding” the pattern.
Investment Casting production process
Investment casting, or lost wax casting, finds applications across various industries for producing complex and high-precision metal components. Here’s a breakdown of the investment casting production process for a more precise understanding:
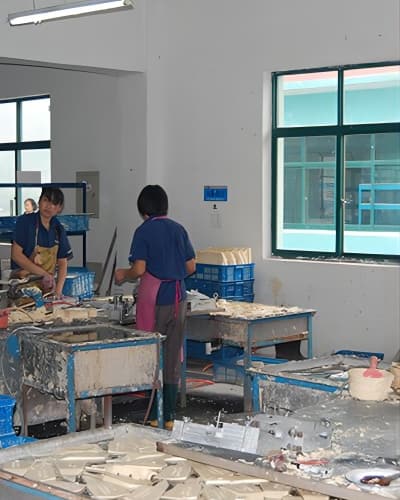
Pattern Creation: The process begins with creating a pattern, typically made of wax or a similar material. This pattern replicates the desired shape of the final metal component.
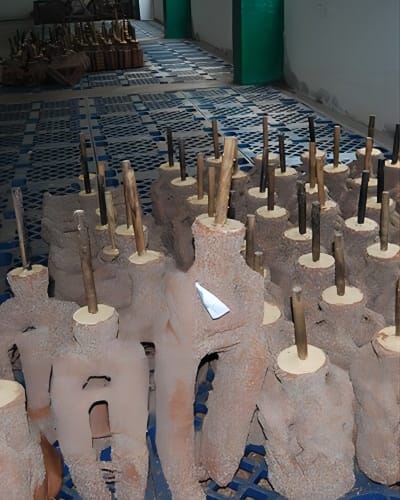
Assembly: Multiple wax patterns, known as the “pattern tree,” are attached to a central wax sprue to form a cluster. Additional wax rods, known as “gates” and “runners,” are attached to facilitate the flow of molten metal during casting.
Shell Building: The wax pattern cluster is dipped into a ceramic slurry multiple times, alternating with the application of refractory materials like sand or stucco. This builds a ceramic shell around the wax patterns, creating a mold.
Dewaxing: Once the ceramic shell is dried and hardened, it undergoes dewaxing. The entire assembly is heated to melt and remove the wax patterns, leaving a cavity in the ceramic shell that mirrors the desired metal component’s shape.
Preheating: The ceramic shell mold is preheated to a specified temperature to prepare it for receiving the molten metal.
Casting: Molten metal, typically aluminium, bronze, brass, or steel, is poured into the preheated ceramic shell mold. The metal fills the cavity previously occupied by the wax pattern, taking its shape.
Cooling and Solidification: After pouring, the molten metal inside the mold cools and solidifies, forming the final metal component.
Shell Removal: Once the metal has cooled sufficiently, the ceramic shell is broken away or dissolved, revealing the solid metal casting inside.
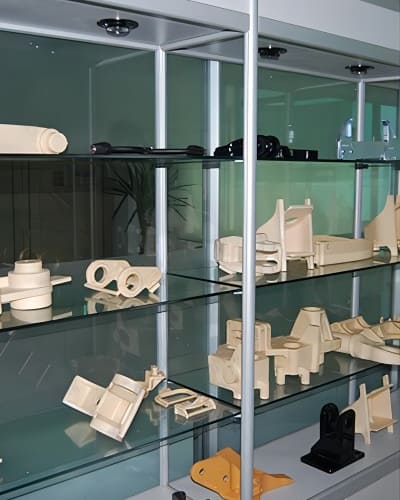
Finishing: The cast metal component undergoes finishing processes such as grinding, machining, polishing, and heat treatment to achieve the desired surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and mechanical properties.
Investment casting is utilized in aerospace, automotive, defence, medical, and jewellery manufacturing industries, where intricate and high-quality metal components are required. Its ability to produce complex shapes with tight tolerances and its versatility in handling various metals make it a preferred choice for many applications.
Advantages Of Investment Casting Process
The investment casting process offers several advantages, making it a preferred method for producing complex metal components. Here are some of the key advantages:
Complex Geometry: Investment casting allows for the production of intricate and complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other manufacturing methods. This includes features such as thin walls, undercuts, and internal cavities.
High Precision: The process provides excellent dimensional accuracy and tight tolerances, resulting in parts with precise specifications and minimal post-processing requirements.
Smooth Surface Finish: Investment castings typically have smooth surface finishes straight from the mold, reducing the need for secondary machining or finishing operations.
Versatility in Materials: Investment casting can be used with a wide range of metals and alloys, including ferrous and non-ferrous metals, stainless steel, aluminum, brass, and titanium, allowing for flexibility in material selection based on application requirements.
Material Savings: The process minimizes material waste since only the required amount of metal is used to form the casting, resulting in cost savings compared to machining from solid stock.
Cost-Effectiveness: Despite the initial tooling and setup costs, investment casting can be cost-effective for producing small to medium-sized production runs of complex parts due to its high efficiency and minimal labor requirements.
Design Freedom: Investment casting offers design freedom, allowing engineers to optimize part designs for performance and functionality without being constrained by traditional manufacturing limitations.
Consistency and Reproducibility: The investment casting process provides consistent and reproducible results from part to part, ensuring uniformity in quality and performance across production batches.
Reduced Assembly: Complex parts that would require multiple components and assembly steps with other manufacturing methods can often be produced as a single, integrated investment casting, reducing assembly time and costs.
Wide Range of Applications: Investment casting is utilized across various industries, including aerospace, automotive, defense, medical, and industrial applications, where high-quality, intricate metal components are required.
Overall, the investment casting process offers a combination of design flexibility, precision, and cost-effectiveness, making it a versatile and valuable manufacturing technique for producing complex metal parts.
Considerations for Using Investment Casting:
Tooling Cost: Permanent tooling can be expensive for low-volume production, but alternatives like SLA or printed patterns may offer cost-effective solutions.
Size Limitations: While investment casting can accommodate a range of sizes, there are limitations compared to other casting methods.
Timing: The multi-step process of investment casting can be time-consuming, although processing times may be shorter than other alternatives.














No comment